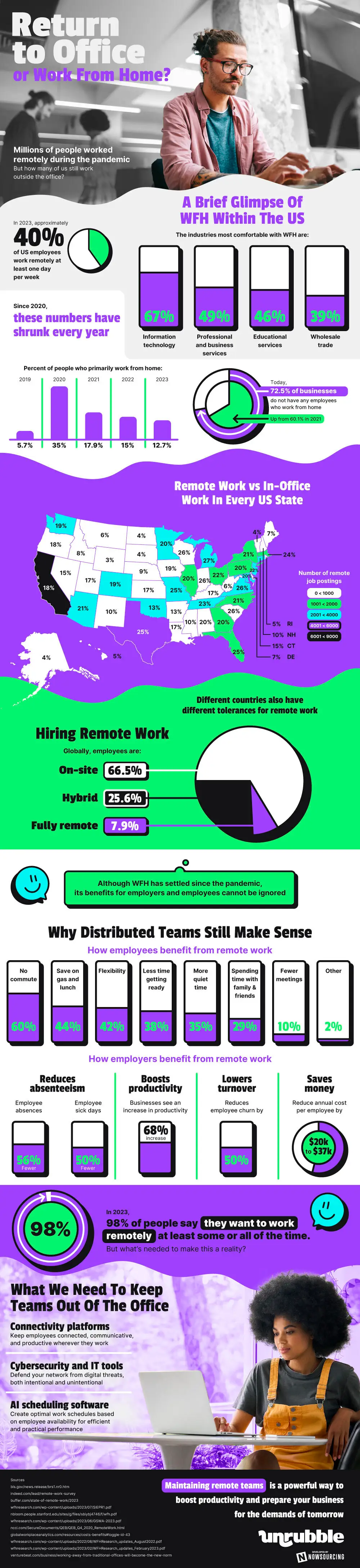
The United States workforce has witnessed a dramatic shift since the pandemic, with remote work now a staple in many sectors. By 2023, around 40% of U.S. employees were working remotely at least once a week. Industries leading this change include Information Technology (67%), Professional and Business Services (49%), and Educational Services (46%). Despite a peak in 2020, the trend has seen a gradual decrease to 12.7% in 2023.
This shift is evident in the fact that 72.5% of businesses now report having no remote employees, a rise from 60.1% in 2021. The state-by-state breakdown shows Michigan at the forefront with 27% remote workers, while Wyoming lags at 3%. Globally, on-site work is still prevalent at 66.5%, but the benefits of remote work remain clear.
Employees enjoy perks like no commute (60%), savings on expenses (44%), and flexibility (42%). Employers also benefit from fewer absences (56% reduction) and sick days (50% reduction), alongside a 68% increase in productivity. In 2023, a significant 98% of people showed a preference for remote work, either full-time or part-time.
To maintain this trend, businesses are focusing on connectivity platforms, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence scheduling software. These tools are essential for a productive, remote workforce, ready for the workforce challenges of tomorrow.